Lifetime Warranty

Hassle Free Returns

Free Resizing

Conflict Free Diamonds
Top Questions and Answers Color Diamonds
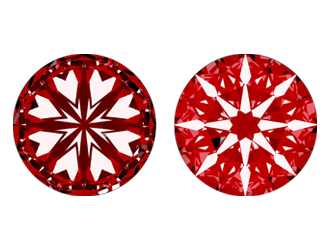
Diamond cut refers to how nicely a diamond has been fashioned and faceted. This element of the diamond’s great is important as it impacts how light is pondered within the diamond, affecting its brilliance and sparkle. A well-cut diamond will replicate mild in a way that maximizes its fire and brilliance, making it more visually attractive. Conversely, a poorly cut diamond can appear dull, irrespective of its coloration or readability.
Diamond reduce is graded based totally on numerous elements which include proportions, symmetry, and polish. The grading scale usually levels from terrific to poor, assessing how nicely the diamond's facets have interaction with light. gear like the GIA (Gemological Institute of the usa) use particular measurements and pointers to evaluate a diamond’s cut. A cut complements the diamond’s ordinary appearance and price, even as a lower grade might diminish its visible effect.
Diamonds are available in diverse reduce patterns, consisting of spherical superb, princess, emerald, and cushion cuts, among others. every style has its own unique characteristics and is chosen based totally on non-public preference and the diamond’s natural attributes. The spherical splendid reduce is the maximum famous and is thought for its high-quality sparkle, at the same time as other cuts just like the emerald or princess reduce provide a distinct aesthetic and attraction.
Whilst a few aspects of a diamond’s reduce can be modified, inclusive of re-sprucing or minor side adjustments, substantial alterations are not commonly possible. A diamond's authentic cut is essentially permanent, and any attempts to modify it can potentially damage the stone. consequently, choosing a diamond with a properly-proportioned cut from the begin is vital for reaching the desired visible impact and value.
The reduce of a diamond is one of the key factors that decide its rate. Diamonds with advanced cuts are regularly priced higher due to their more desirable brilliance and visual appeal. A cut maximizes the diamond’s potential, making it greater applicable and, consequently, more costly. then again, diamonds with lower cut grades might be much less high-priced, however they will also lack the equal level of brilliance and beauty.